1. Machine code
Generate assembly code mstore.s:
1
$ gcc -Og -S mstore.c
Generate an object-code file mstore.o:
1
$ gcc -Og -c mstore.c
Check byte-encoding instructions, disassembler:
1
$ objdump -d mstore.o
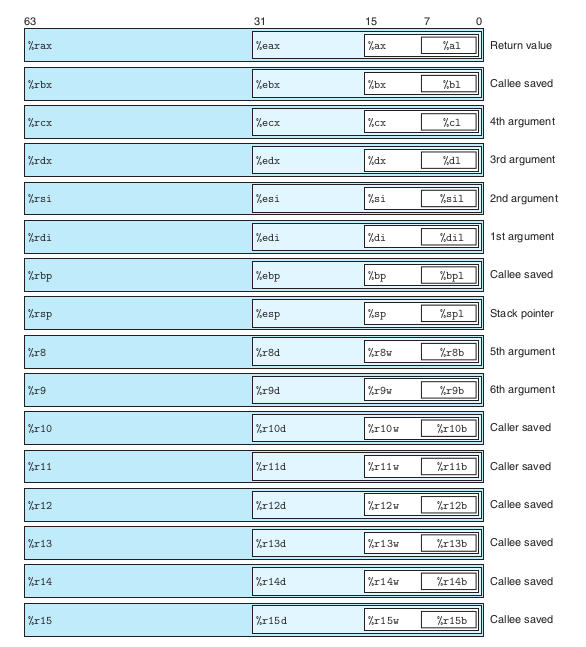
The original 8086 had 16-bit registers, from %ax through %bp; with the extension to IA32, these registers were expanded to 32-bit registers, as labeled %eax through %ebp. For x86-64, they begin with %r.
Data movement Instructions
Data movement instruction has four variants, movb, movw, movl, movq, differing in their source and destination types, what conversions they perform, and other side effects they may have.
Convension 1: x86-64 imposes the restriction that a move instruction cannot have both operands refer to memory location.
Convension 2: For most cases, MOV will only update the specific register bytes or memory locations indicated by the destination operand. The only exception is that when movl has a register as the destination, it will also set the high-order 4 bytes of the register to 0.
TBC.
Copyright: all contents are from CS:APP3e.
